📘 Backend/Java
Java 객체 지향 프로그래밍 - 2
신건우
2023. 4. 1. 11:14
📘 다형성
- 한 타입의 참조변수를 통해 여러타입의 객체를 참조할 수 있도록 만든 것
- 상위 클래스 타입의 참조변수를 통해서 하위 클래스의 객체를 참조할 수 있도록 허용한 것
ex) Friend girlfriend = new GirlFriend(); 객체 타입과 참조변수 타입 불일치
//참조변수의 다형성 예시
class Friend {
public void friendInfo() {
System.out.println("나는 당신의 친구입니다.");
}
}
class BoyFriend extends Friend {
public void friendInfo() {
System.out.println("나는 당신의 남자친구입니다.");
}
}
class GirlFriend extends Friend {
public void friendInfo() {
System.out.println("나는 당신의 여자친구입니다.");
}
}
public class FriendTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Friend friend = new Friend(); // 객체 타입과 참조변수 타입의 일치
BoyFriend boyfriend = new BoyFriend();
Friend girlfriend = new GirlFriend(); // 객체 타입과 참조변수 타입의 불일치
friend.friendInfo();
boyfriend.friendInfo();
girlfriend.friendInfo();
}
}ex) GirlFriend friend1 = new Friend(); ↑ 의 반대로 상위클래스는 하위클래스 타입의 객체 참조 불가능
public class FriendTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Friend friend = new Friend(); // 객체 타입과 참조변수 타입의 일치 -> 가능
BoyFriend boyfriend = new BoyFriend();
Friend girlfriend = new GirlFriend(); // 객체 타입과 참조변수 타입의 불일치 -> 가능
// GirlFriend friend1 = new Friend(); -> 하위클래스 타입으로 상위클래스 객체 참조 -> 불가능
friend.friendInfo();
boyfriend.friendInfo();
girlfriend.friendInfo();
}
}참조변수의 타입 변환 3가지 조건
- 서로 상속관계인 상위 - 하위 클래스 사이에만 타입 변환 가능
- 하위 클래스에서 상위클래스 타입으로 타입변환(업캐스팅)은 형변환 연산자()를 생락할 수 있음
- 반대로 상위 - 하위클래스 타입으로 변환(다운캐스팅)은 형변환 연산자() 필수 명시
참조변수의 타입 변환 = 사용할 수 있는 멤버의 개수 조절
public class VehicleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
Vehicle vehicle = (Vehicle) car; // 상위 클래스 Vehicle 타입으로 변환(생략 가능)
Car car2 = (Car) vehicle; // 하위 클래스 Car타입으로 변환(생략 불가능)
MotorBike motorBike = (MotorBike) car; // 상속관계가 아니므로 타입 변환 불가 -> 에러발생
}
}
class Vehicle {
String model;
String color;
int wheels;
void startEngine() {
System.out.println("시동 걸기");
}
void accelerate() {
System.out.println("속도 올리기");
}
void brake() {
System.out.println("브레이크!");
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
void giveRide() {
System.out.println("다른 사람 태우기");
}
}
class MotorBike extends Vehicle {
void performance() {
System.out.println("묘기 부리기");
}
}instanceof 연산자
- 캐스팅이 가능한 지 여부를 boolean 타입으로 확인
- 참조변수 instanceof 타입 을 입력했을때 리턴 값이 true가 나오면 타입 변환 가능
public class InstanceOfExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Animal();
System.out.println(animal instanceof Object); //true
System.out.println(animal instanceof Animal); //true
System.out.println(animal instanceof Bat); //false
Animal cat = new Cat();
System.out.println(cat instanceof Object); //true
System.out.println(cat instanceof Animal); //true
System.out.println(cat instanceof Cat); //true
System.out.println(cat instanceof Bat); //false
}
}
class Animal {};
class Bat extends Animal{};
class Cat extends Animal{};다형성의 활용 예시
class Coffee {
int price;
public Coffee(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
class Americano extends Coffee {};
class CaffeLatte extends Coffee {};
class Customer {
int money = 50000;
void buyCoffee(Americano americano) { // 아메리카노 구입
money = money - americano.price;
}
void buyCoffee(CaffeLatte caffeLatte) { // 카페라테 구입
money = money - caffeLatte.price;
}
}위의 코드에서 Customer 의 기능이 현재는 2가지 지만 종류가 많다면 코드가 복잡해질 것이다.
이때 다형성을 활용하여 아래와 같이 수정할 수 있다.
void buyCoffee(Coffee coffee) { // 매개변수의 다형성
money = money - coffee.price;
}전체적인 흐름을 다시 보자
package package2;
public class PolymorphismEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.buyCoffee(new Americano());
customer.buyCoffee(new CaffeLatte());
System.out.println("현재 잔액은 " + customer.money + "원 입니다.");
}
}
class Coffee {
int price;
public Coffee(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
class Americano extends Coffee {
public Americano() {
super(4000); // 상위 클래스 Coffee의 생성자를 호출
}
public String toString() {return "아메리카노";}; //Object클래스 toString()메서드 오버라이딩
};
class CaffeLatte extends Coffee {
public CaffeLatte() {
super(5000);
}
public String toString() {return "카페라떼";};
};
class Customer {
int money = 50000;
void buyCoffee(Coffee coffee) {
if (money < coffee.price) { // 물건 가격보다 돈이 없는 경우
System.out.println("잔액이 부족합니다.");
return;
}
money = money - coffee.price; // 가진 돈 - 커피 가격
System.out.println(coffee + "를 구입했습니다.");
}
}📘 추상화
- 사물이나 표상을 어떤 성질,공통성, 본질의 형태를 추출하는것
- 기존 클래스간 공통적인 속성을 찾아내서 상위의 클래스을 만드는 작업
- 공통적인 속성,기능을 모아 하위클래스 & 상위클래스를 정의 가능
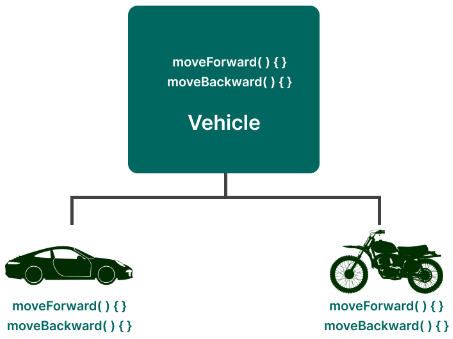
이동수단의 공통적인 부분을 Vehicle 클래스로 정의
abstract
기타제어자 중 제일 많이 쓰이는 제어자
- 자바에서에 의미는 '미완성' 이라는 의미를 가짐
- 메소드 앞에 붙을경우 '추상메소드', 클래스 앞에 붙을경우 '추상클래스' 라고 불림
- 어떤 클래스에 추상메소드가 포함되어있으면 그 클래스는 자동으로 추상클래스가 됨
abstract class AbstractExample { // 추상 메서드가 최소 하나 이상 포함돼있는 추상 클래스
abstract void start(); // 메서드 바디가 없는 추상메서드
}abstract class
- 메소드 바디가 선언되어있지 않은 추상 메소드를 포함하는 '미완성 설계도'
- 미완성된 구조를 가지고 있기에 객체 생성이 불가능하다
- 그럼 왜 사용할까? 상속 관계에 있어서 새로운 클래스를 작성하는데 매우 유용함
abstract class Animal {
public String kind;
public abstract void sound();
}
class Dog extends Animal { // Animal 클래스로부터 상속
public Dog() {
this.kind = "포유류";
}
public void sound() { // 메서드 오버라이딩 -> 구현부 완성
System.out.println("멍멍");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal { // Animal 클래스로부터 상속
public Cat() {
this.kind = "포유류";
}
public void sound() { // 메서드 오버라이딩 -> 구현부 완성
System.out.println("야옹");
}
}
class DogExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Animal dog = new Dog();
dog.sound();
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.sound();
}
}공통적인 특성을 추상클래스에 선언한 후, 상속된 하위클래스에서 오버라이딩을 통해 구체적인 내용 선언
상층부에 가까울수록 추상화 , 하층부에 가까울수록 구체화 되는 특성이 있음
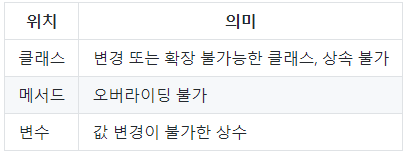
final
- 필드,지역변수,클래스 앞에 위치하며 위치에 따라 의미가 조금씩 달라짐
공통적으로 변경 & 확장이 불가능
final class FinalEx { // 확장/상속 불가능한 클래스
final int x = 1; // 변경되지 않는 상수
final int getNum() { // 오버라이딩 불가한 메서드
final int localVar = x; // 상수
return x;
}
}인터페이스
추상 메소드의 집합
- 추상화를 구현하는데 활용되며, 추상클래스에 비해 더 높은 추상성을 가짐
- 추상 메소드와 상수'만'을 멤버로 가질 수 있음
기본 구조
- 내부의 모든 필드가 public static final로 정의됨 (생략가능)
- static,default 이외의 모든 메소드가 public abstract로 정의됨 (생략가능)
public interface InterfaceEx {
public static final int rock = 1; // 인터페이스 인스턴스 변수 정의
final int scissors = 2; // public static 생략
static int paper = 3; // public & final 생략
public abstract String getPlayingNum();
void call() //public abstract 생략
}상수 = public static final / 메소드 = public abstract
인터페이스의 구현
implements 키워드
- 추상클래스와 마찬가지로 인스턴스 생성 X , 메소드 바디를 정의하는 클래스를 따로 작성해야함
class 클래스명 implements 인터페이스명 {
... // 인터페이스에 정의된 모든 추상메서드 구현
}특정 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스는 해당 인터페이스에 정의된 모든 추상메소드를 구현해야함
어떤 클래스가 특정 인터페이스를 구현한다는건
그 클래스에게 인터페이스의 추상 메소드를 반드가 구현하도록 강제하며,
모든 추상메소드들을 해당 클래스 내에서 오버라이딩하여 바디를 완성한다 는의미를 가짐
인터페이스 다중 구현
- 클래스간에는 다중상속이 허용되지 않지만 인터페이스는 다중적 구현이 가능함
- 즉, 하나의 클래스가 여러개의 인터페이스 구현 가능, but 인터페이스 끼리만 상속이 가능하고 Object와의 관계가 없음
class ExampleClass implements ExampleInterface1, ExampleInterface2, ExampleInterface3 {
... 생략 ...
}
interface Animal { // 인터페이스 선언. public abstract 생략 가능.
public abstract void cry();
}
interface Pet {
void play();
}
class Dog implements Animal, Pet { // Animal과 Pet 인터페이스 다중 구현
public void cry(){ // 메서드 오버라이딩
System.out.println("멍멍!");
}
public void play(){ // 메서드 오버라이딩
System.out.println("원반 던지기");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal, Pet { // Animal과 Pet 인터페이스 다중 구현
public void cry(){
System.out.println("야옹~!");
}
public void play(){
System.out.println("쥐 잡기");
}
}
public class MultiInheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
Cat cat = new Cat();
dog.cry();
dog.play();
cat.cry();
cat.play();
}
}
// 출력값
멍멍!
원반 던지기
야옹~!
쥐 잡기